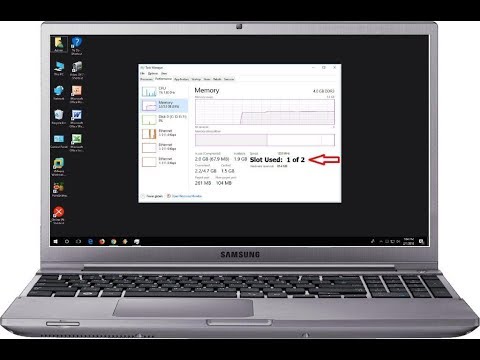
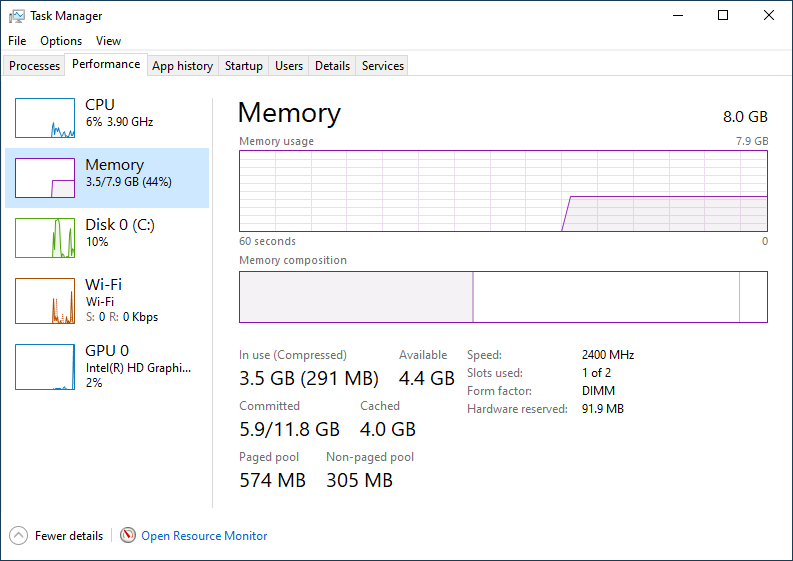
Followed by the scan results. As first it looks a little confusing, but if you scroll down to the second boxed results on the page, you will see your computer memory information, including the number of memory slots used and available. As you can see on my laptop that I am using, both memory slots are being used. The typical home computer comes with Win7x64 Home Premium which only supports using up to 16Gb ram. It’s sure OK to install more than 16Gb ram (assuming the motherboard supports it), but Win7x64 Home Premium will limit itself to using only 16Gb ram. To use more than 16Gb ram in Win7x64, you need Pro or Ultimate or Enterprise versions.
The total amount of memory, or RAM, a computer can have is dependent on the motherboard installed in the computer and the operating system. In general, most motherboards will support either two or four memory modules, but the type and amount of memory can differ widely from one motherboard to the next.
I don't know how you can find out how many slots are in use, but you can find out the # of slots and RAM requirements by getting the motherboard make and model from System Info and then looking up the motherboard on the manufacturers web site.
 Tip
TipIf you are trying to find memory specifications for upgrading your computer memory, see: What type of computer memory to use in a memory upgrade?
NoteIf you are not sure what operating system you have, see: How to find what operating system is on a computer.
Microsoft Windows computers
How much ram your computer can hold depends on if you're running a 32 or 64-bit version of Windows, which depends on your CPU. The capacities are as follows, permitting you have the physical space to fit the RAM modules.
- 32-bit systems - up to 4 GB
- 64-bit systems - up to 128 GB
How to find out if you have a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows
- Press the Windows key and the Pause/Break key at the same time.
- A new window should appear that says System at the top, similar to the one below.
- Under the System section, next to System type:, you can see if your version of Windows is 32-bit or 64-bit.
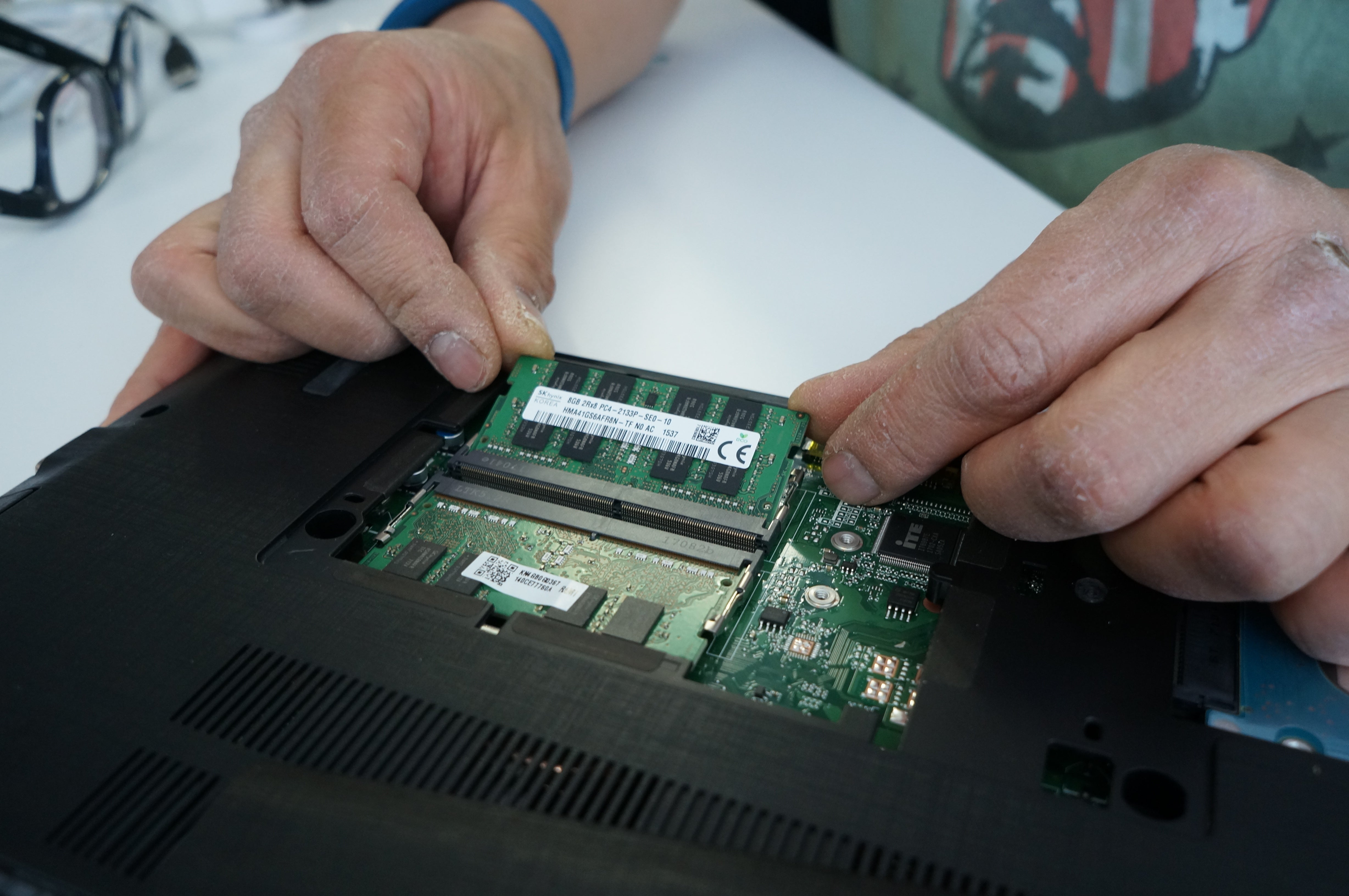
Once you know the type of memory and the total amount of memory the computer supports, you can increase the amount of memory by installing additional sticks of RAM. You can also replace existing sticks of RAM with ones having a higher amount of memory.

Apple macOS computers
- Click the Apple icon in the upper-left corner to open the Apple menu.
- In the drop-down menu that appears, select About This Mac.
- You should see a window open that is similar to the one below.
- Visit Apple's page for a table containing the max RAM for each machine, based on the information in the iMac section in the above window.
Once you know the type of memory and the total amount of memory the computer supports, you can increase the amount of memory by installing additional sticks of RAM. You can also replace existing sticks of RAM with ones having a higher amount of memory.
Linux and Unix-based computers


Similar to a Windows-based computer, Linux-based machines' maximum RAM is based on whether they have 32-bit or 64-bit architecture. Most 32-bit Linux systems only support 4 GB of RAM, unless the PAE kernel is enabled, which allows a 64 GB max. However, 64-bit variants support between 1 and 256 TB.
How To Find Out How Many Ram Slots Are Used Per
To determine how much ram your Linux-based computer supports, open the Terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and type in the following command:
Look for the Maximum Capacity section to see the limit on RAM.
Once you know the type of memory and the total amount of memory the computer supports, you can increase the amount of memory by installing additional sticks of RAM. You can also replace existing sticks of RAM with ones having a higher amount of memory.
How To Find Out How Many Ram Slots Are Used To
Additional information
How To Find Out How Many Ram Slots Are Used For A
- See the RAM and memory definition for further information about each of these terms and related links.